|
To facilitate drug screening for this pathogen we developed and validated an automated, high throughput screening methodology. We identified Corifungin (Acea Biosciences), a water-soluble polyene macrolide, with better activity against Naegleria fowleri than Amphotericin B. In vivo efficacy of Corifungin in a mouse model of Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) was confirmed by absence of detectable amebae in brain and 100% survival of mice for 17 days post-infection at a single intraperitoneal dose of 9 mg/kg/day for 10 days. As shown in Panel B, in mice treated with Corifungin there are multiple spherical inflammatory foci (arrows) but no viable trophozoites. Most importantly brain tissue is well preserved with no evidence of tissue necrosis. The same dose of Amphotericin B (Panel A) did not reduce ameba growth and mouse survival was compromised. In Panel A, brain tissue has abundant amebae (arrow-heads) and widespread tissue necrosis.
Considering its in vitro and in vivo efficacy and recent Orphan-Drug Designation by the US FDA, Corifungin is a novel and promising therapeutic option for PAM.
The target-based approach is used in CDIPD to validate sterol biosynthesis pathway in N. fowleri as potential therapeutic drug target. Inhibitors with known mechanism of action (MOA) against a variety of sterol biosynthetic enzymes are assessed in vitro and in vivo to chemically validate the targets and re-purpose existing drugs for the treatment of PAM.
 |
|||
|
|
|
|
PUBLICATIONS
Identification of Four Amoebicidal Nontoxic Compounds by a Molecular Docking Screen of Naegleria fowleri Sterol Δ8-Δ7-Isomerase and Phenotypic Assays. ACS Infect Dis. 2019 Oct 17. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00227. [Epub ahead of print] Shi D, Chahal KK, Oto P, Nothias LF, Debnath A, McKerrow JH, Podust LM, Abagyan R.
Enzymatic chokepoints and synergistic drug targets in the sterol biosynthesis pathway of Naegleria fowleri. PLoS Pathog. 2018 Sep 13;14(9):e1007245. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007245. eCollection 2018 Sep. Zhou W, Debnath A, Jennings G, Hahn HJ, Vanderloop BH, Chaudhuri M, Nes WD, Podust LM.
CYP51 is an essential drug target for the treatment of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Dec 28;11(12):e0006104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006104. eCollection 2017 Dec. Debnath A, Calvet CM, Jennings G, Zhou W, Aksenov A, Luth MR, Abagyan R, Nes WD, McKerrow JH, Podust LM.
Naegleria fowleri after 50 Years: Is it a neglected pathogen? J Med Microbiol. 2016 Jul 4. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000303. [Epub ahead of print] Martínez-Castillo M, Cárdenas-Zúñiga R, Coronado-Velázquez D, Debnath A, Serrano-Luna J, Shibayama M.
In vitro efficacy of corifungin against Acanthamoeba castellanii trophozoites and cysts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(3):1523-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02254-13. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Debnath A, Tunac JB, Silva-Olivares A, Galindo-Gómez S, Shibayama M, McKerrow JH.
Corifungin, a new drug lead against Naegleria, identified from a high-throughput screen. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Nov;56(11):5450-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00643-12. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Debnath A, Tunac JB, Galindo-Gómez S, Silva-Olivares A, Shibayama M, McKerrow JH.

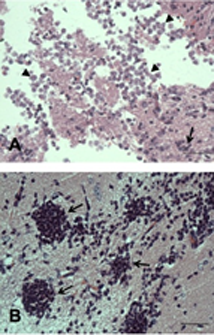 Brain tissue in mice infected with Naegleria fowleri and treated with Amphotericin B (A) or Corifungin (B).
Brain tissue in mice infected with Naegleria fowleri and treated with Amphotericin B (A) or Corifungin (B).