|
Our research on Entamoeba histolytica includes understanding how specific host factors influence the transcriptional program of E. histolytica and protease activity related to intestinal invasion. In collaboration with Sharon Reed of University of California, San Diego, we are studying the role of cysteine proteases in amebiasis.
In parallel, we pioneered the development of a high throughput assay for screening potential drugs against Entamoeba in culture. Utilizing this automated screening methodology we recently identified auranofin, an FDA-approved oral drug, as 10 times more effective in culture than metronidazole, the current drug of choice for amebiasis. Auranofin has been in clinical use to treat rheumatoid arthritis since 1985. Our studies indicated that auranofin targets the E. histolytica thioredoxin reductase. Oral auranofin at low dose significantly decreased the number of parasites and also host inflammation in a mouse model of colitis and a hamster model of amebic liver abscess. A similar dose of metronidazole had no effect. These findings suggest that thioredoxin reductase is a valid drug target in E. histolytica, which can be inhibited with a "repurposed" FDA approved drug, auranofin. Based on these results, the US FDA has given Orphan-Drug status to auranofin for treatment of amebiasis. A Phase II clinical trial of auranofin for human amebiasis is currently being planned by Dr. Reed.
 |
|||
|
|
|
|
PUBLICATIONS
Nitroimidazole carboxamides as antiparasitic agents targeting Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica and Trichomonas vaginalis. Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Sep 14;120:353-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.04.064. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Jarrad AM, Debnath A, Miyamoto Y, Hansford KA, Pelingon R, Butler MS, Bains T, Karoli T, Blaskovich MA, Eckmann L, Cooper MA.
X-ray structures of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase from Entamoeba histolytica and prevailing hypothesis of the mechanism of Auranofin action. J Struct Biol. 2016 May;194(2):180-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Parsonage D, Sheng F, Hirata K, Debnath A, McKerrow JH, Reed SL, Abagyan R, Poole LB, Podust LM.
Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors repurposed against Entamoeba histolytica. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:368. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00368. Shahinas D, Debnath A, Benedict C, McKerrow JH, Pillai DR.
Hsp90 inhibitors as new leads to target parasitic diarrheal diseases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Jul;58(7):4138-44. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02576-14. Epub 2014 May 12. Debnath A, Shahinas D, Bryant C, Hirata K, Miyamoto Y, Hwang G, Gut J, Renslo AR, Pillai DR, Eckmann L, Reed SL, McKerrow JH.
A reprofiled drug, auranofin, is effective against metronidazole-resistant Giardia lamblia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 May;57(5):2029-35. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01675-12. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Tejman-Yarden N, Miyamoto Y, Leitsch D, Santini J, Debnath A, Gut J, McKerrow JH, Reed SL, Eckmann L.
Reprofiled drug targets ancient protozoans: drug discovery for parasitic diarrheal diseases. Gut Microbes. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):66-71. doi: 10.4161/gmic.22596. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Review. Debnath A, Ndao M, Reed SL.
A high-throughput drug screen for Entamoeba histolytica identifies a new lead and target. Nat Med. 2012 Jun;18(6):956-60. doi: 10.1038/nm.2758. Debnath A, Parsonage D, Andrade RM, He C, Cobo ER, Hirata K, Chen S, García-Rivera G, Orozco E, Martínez MB, Gunatilleke SS, Barrios AM, Arkin MR, Poole LB, McKerrow JH, Reed SL.
An image-based assay for high throughput screening of Giardia lamblia. J Microbiol Methods. 2011 Mar;84(3):398-405. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2010.12.026. Epub 2011 Jan 22. Gut J, Ang KK, Legac J, Arkin MR, Rosenthal PJ, McKerrow JH.
Novel non-peptidic vinylsulfones targeting the S2 and S3 subsites of parasite cysteine proteases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Nov 1;19(21):6218-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.08.098. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Bryant C, Kerr ID, Debnath M, Ang KK, Ratnam J, Ferreira RS, Jaishankar P, Zhao D, Arkin MR, McKerrow JH, Brinen LS, Renslo AR.
A contiguous compartment functions as endoplasmic reticulum and endosome/lysosome in Giardia lamblia. Eukaryot Cell. 2009 Nov;8(11):1665-76. doi: 10.1128/EC.00123-09. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Abodeely M, DuBois KN, Hehl A, Stefanic S, Sajid M, DeSouza W, Attias M, Engel JC, Hsieh I, Fetter RD, McKerrow JH.
Identification of the major cysteine protease of Giardia and its role in encystation. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 27;283(26):18024-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802133200. Epub 2008 Apr 29. DuBois KN, Abodeely M, Sakanari J, Craik CS, Lee M, McKerrow JH, Sajid M.
Transcriptional and secretory responses of Entamoeba histolytica to mucins, epithelial cells and bacteria. Int J Parasitol. 2007 Jul;37(8-9):897-906. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Debnath A, Tashker JS, Sajid M, McKerrow JH.
A phagocytosis mutant of Entamoeba histolytica is less virulent due to deficient proteinase expression and release. Exp Parasitol. 2007 Feb;115(2):192-9. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Hirata KK, Que X, Melendez-Lopez SG, Debnath A, Myers S, Herdman DS, Orozco E, Bhattacharya A, McKerrow JH, Reed SL.
Giardia lamblia cysteine proteases. Parasitol Res. 2006 Sep;99(4):313-6. Epub 2006 Apr 6. Review. No abstract available. DuBois KN, Abodeely M, Sajid M, Engel JC, McKerrow JH.
Entamoeba histolytica: Characterization of human collagen type I and Ca2+ activated differentially expressed genes. Exp Parasitol. 2005 Jul;110(3):214-9. Epub 2005 Apr 8. Debnath A, Akbar MA, Mazumder A, Kumar S, Das P.
Identification of genomic responses to collagen binding by trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 2004 Aug 1;190(3):448-57. Epub 2004 Jul 2. Debnath A, Das P, Sajid M, McKerrow JH.
A surface amebic cysteine proteinase inactivates interleukin-18. Infect Immun. 2003 Mar;71(3):1274-80. Que X, Kim SH, Sajid M, Eckmann L, Dinarello CA, McKerrow JH, Reed SL.
Homology modeling of Entamoeba histolytica cysteine proteinases reveals the basis for cathepsin L-like structure with cathepsin B-like specificity. Arch Med Res. 2000 Jul-Aug;31(4 Suppl):S63-4. No abstract available. Brinen LS, Que X, McKerrow JH, Reed SL.
A primitive enzyme for a primitive cell: the protease required for excystation of Giardia. Cell. 1997 May 2;89(3):437-44. Ward W, Alvarado L, Rawlings ND, Engel JC, Franklin C, McKerrow JH.
Pathogenesis in amebiasis: is it genetic or acquired? Infect Agents Dis. 1992 Feb;1(1):11-4. Review. No abstract available. McKerrow JH.
A unique cysteine proteinase gene of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica correlates with virulence. Arch Med Res. 1992;23(2):181-2. Reed S, Bouvier J, Hirata K, Que X, Pollack AS, Engel JC, Gillin F, McKerrow JH.
Detection of HIV-1 in Entamoeba histolytica without evidence of transmission to human cells. AIDS. 1991 Jan;5(1):93-6. Brown M, Reed S, Levy JA, Busch M, McKerrow JH.
Entamoeba histolytica: correlation of the cytopathic effect of virulent trophozoites with secretion of a cysteine proteinase. Exp Parasitol. 1990 Aug;71(2):199-206. Keene WE, Hidalgo ME, Orozco E, McKerrow JH.
[Direct relation between secretion of proteolytic enzymes and virulence in Entamoeba histolytica]. Arch Invest Med (Mex). 1990;21 Suppl 1:133-8. Spanish. No abstract available. Hidalgo ME, Hernández R, Keene WE, McKerrow JH, Orozco E.
Thiol proteinase expression and pathogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2772-7. Reed SL, Keene WE, McKerrow JH.
Cleavage of C3 by a neutral cysteine proteinase of Entamoeba histolytica. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):189-95. Reed SL, Keene WE, McKerrow JH, Gigli I.
The major neutral proteinase of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):536-49. Keene WE, Petitt MG, Allen S, McKerrow JH.

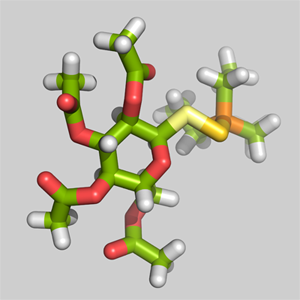 3-D structure of the Auranofin molecule with gold atom in dark-yellow bound between the light-yellow sulfur and orange posphorus.
3-D structure of the Auranofin molecule with gold atom in dark-yellow bound between the light-yellow sulfur and orange posphorus.